With the rapid advancement of artificial intelligence and robotics, humanoid robots are moving beyond laboratory environments and into real-world applications. In the United States, humanoid robots are increasingly being deployed across research institutions, corporate campuses, retail services, education and training, and even home assistance scenarios.
Compared with traditional automated equipment, humanoid robots feature far more complex mechanical structures, higher degrees of freedom, and movement patterns that closely resemble human behavior. These characteristics place significantly higher demands on the energy system that powers them.
In real-world use, many users have gradually realized that the true limiting factor for humanoid robot efficiency is not computing power or hardware capability, but whether runtime can remain stable and reliable over time. The humanoid robot battery ultimately determines how long a robot can operate, how far it can move, and whether it can continuously complete assigned tasks.
Why Runtime Has Become One of the Top Concerns for Humanoid Robot Users
Unlike conventional electronic devices, humanoid robots exhibit a clear pattern of multi-dimensional energy consumption.
During operation, a humanoid robot must not only supply power to its main control and computing units, but also continuously support multiple joint drive motors, sensor systems, vision modules, and communication units. In real-world usage scenarios, this challenge becomes especially pronounced.
1. Usage Duration Is Often Unpredictable
Whether in university laboratories conducting algorithm debugging or in corporate showrooms and shopping malls performing demonstrations and interactions, humanoid robots are frequently required to remain powered on for long periods and enter active working states at any moment.
In academic research environments, a complete algorithm test or model iteration cycle typically requires 6–10 hours of continuous power-on time.
In exhibition halls or commercial demonstration settings, humanoid robots are often expected to operate 8–12 hours per day, combining extended low-power standby with intermittent high-power motion bursts.
If a humanoid robot battery exhibits a relatively high self-discharge rate during low-load standby—such as 1%–2% capacity loss per hour—the actual usable runtime can be significantly reduced.
2. Frequent Changes in Motion Intensity and Load
When humanoid robots walk, turn, grasp objects, or interact with people, they frequently generate instantaneous high-power output, placing extremely high demands on battery discharge stability.
Taking a typical bipedal humanoid robot as an example:
- Normal walking power consumption: approximately 200W–350W
- Instantaneous power during rapid turns or start-up: up to 500W–700W
- Single-arm grasping of 2–5 kg objects: joint motor power increases by 30%–60%
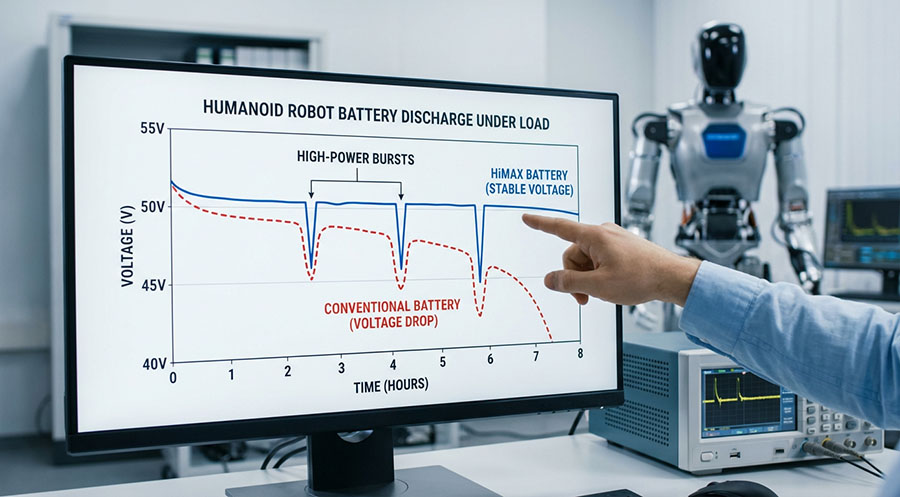
Under such high-frequency power fluctuations, if a humanoid robot battery experiences significant voltage drop at discharge rates above 3C, the drive control system may enter protection mode, forcing motion to slow down or even stop entirely.
3. More Complex Operating Environments
In the United States, humanoid robots are not limited to indoor environments. They are increasingly deployed for outdoor inspection, campus guidance, and semi-open testing scenarios. These applications often involve:
- A wider ambient temperature range: -5°C to 40°C
- Complex ground conditions that increase walking energy consumption by 10%–25%
- Limited opportunities for frequent charging, raising the requirement for single-cycle runtime
In low-temperature conditions, conventional lithium batteries often experience an effective capacity reduction of 15%–30%.
If internal resistance rises noticeably during the mid-to-late stages of discharge, usable output power is further constrained.
4. Mid-to-Late Discharge Performance Determines Whether Tasks Can Be Completed
When these factors combine, any significant performance degradation during the 40%–20% battery level range can directly impact real-world humanoid robot performance. Common issues include:
- Motion response delays increasing by 100–300 milliseconds
- Walking speed reductions of 10%–20%
- Restrictions on complex movements such as turning or grasping
- Forced early shutdowns or return-to-charge interruptions during demonstrations or tasks
For U.S. users who value continuity and operational stability, these issues are far more problematic than a slightly lower nominal battery capacity.
The Core Advantages of HiMAX Batteries in Humanoid Robot Runtime
From the outset, HiMAX batteries were not designed simply to maximize nominal capacity. Instead, they focus on high-load stability, sustained output capability, and real-world usable energy, making them particularly well suited for complex energy systems such as humanoid robots.
In real-world operational testing, when humanoid robots equipped with HiMAX batteries operate under continuous walking and frequent motion conditions, output remains notably stable. Under medium-to-high load scenarios, voltage fluctuation is effectively controlled, allowing both drive systems and computing units to operate consistently within optimal efficiency ranges.
In addition, during instantaneous high-power demand situations—such as start-up, slope climbing, or multi-joint synchronized movements—HiMAX batteries align more effectively with motor control system requirements. This reduces unnecessary energy loss and extends overall operating time.
More importantly, HiMAX batteries emphasize “usable runtime” rather than purely “rated runtime.” With the same design capacity, a higher proportion of energy remains accessible, enabling humanoid robots to maintain stable motion and responsiveness even during the mid-to-late discharge stages.
Case-1: Humanoid Robot Research in University Laboratories
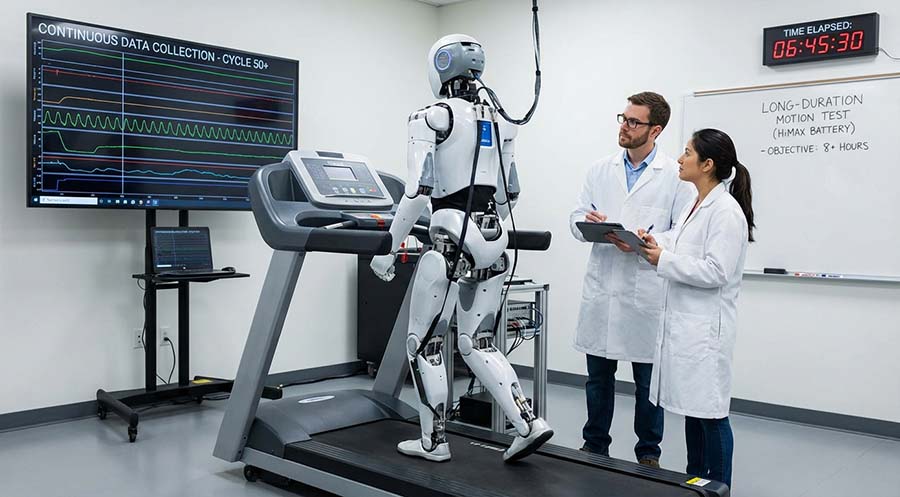

Across many universities and research institutions, humanoid robots are widely used for motion control, artificial intelligence, and human–robot interaction research. These studies often require robots to perform repetitive movements over extended periods while collecting large volumes of data.
A researcher from a university on the U.S. West Coast reported that with conventional battery solutions, their humanoid robot typically needed to stop for charging after only two to three hours of continuous operation. This not only reduced research efficiency but also disrupted experimental workflows.
After switching to a robot platform equipped with HiMAX batteries, the same experimental processes were able to run for significantly longer periods. Even after multiple walking cycles and complex motion tests, the robot maintained stable operation, reducing interruptions caused by insufficient battery power.
This level of runtime stability allowed researchers to focus more on algorithm development rather than constantly monitoring battery levels.
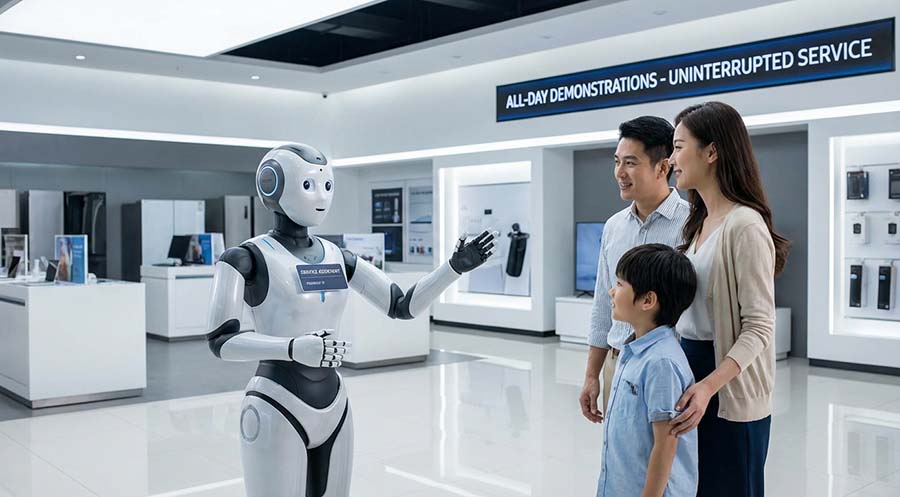
Case-2: Continuous Operation in Commercial Display and Service Scenarios
In commercial applications, such as showroom demonstrations, corporate reception areas, and retail interaction spaces, humanoid robots represent a classic high-frequency usage scenario. In these environments, robots must remain on standby for long periods while responding instantly to user commands with speech and physical movements.
One operator responsible for humanoid robot demonstrations noted that during peak hours, robots previously needed to go offline early for charging, disrupting the continuity of presentations. After adopting HiMAX batteries, the robots were able to maintain smooth motion and timely responses throughout several consecutive hours of demonstrations and interactions, without noticeable performance degradation.
For commercial scenarios, this improvement in runtime translates not only into longer operating hours, but also into greater consistency in service quality.
What Does Extended Runtime Mean for Humanoid Robots?

For humanoid robots, extended runtime represents far more than just additional operating time.
It means:
- Smoother, more human-like motion
- More complete task execution and higher system reliability
- Broader application scenarios with better cost control
HiMAX batteries provide a solid energy foundation for humanoid robots in real, complex, and high-intensity use cases.
By enabling humanoid robots to move from “frequent compromise” to “sustained operation,” and from “demonstration devices” toward “reliable tools,” HiMAX batteries demonstrate long-term, sustainable value within the humanoid robotics field—grounded firmly in real-world application performance.
Find articles related to HiMAX success stories