Battery users often ask: “Why does an old Li-ion battery take so long to charge?” This is a common concern for anyone using rechargeable electronics. As lithium-ion batteries age, the charging process becomes slower, even when the remaining capacity is significantly reduced. This phenomenon is often referred to as the “old-man syndrome.”
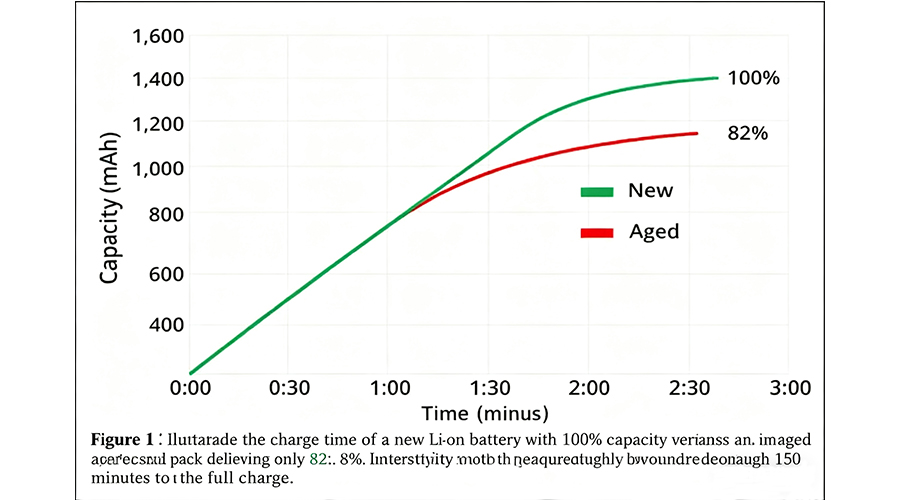
Figure 1 illustrates the charge time of a new Li-ion battery with 100% capacity versus an aged pack delivering only 82%. Interestingly, both require roughly 150 minutes to reach full charge.
New vs. Aged Li-ion Batteries Charging Performance
Figure 1: New and aged Li-ion batteries charging performance [1]
Both packs take about 150 minutes to charge. The new pack charges to 1,400mAh (100%), while the aged one only reaches 1,150mAh (82%).
Why Does Charging Slow Down in Old Li-ion Batteries?
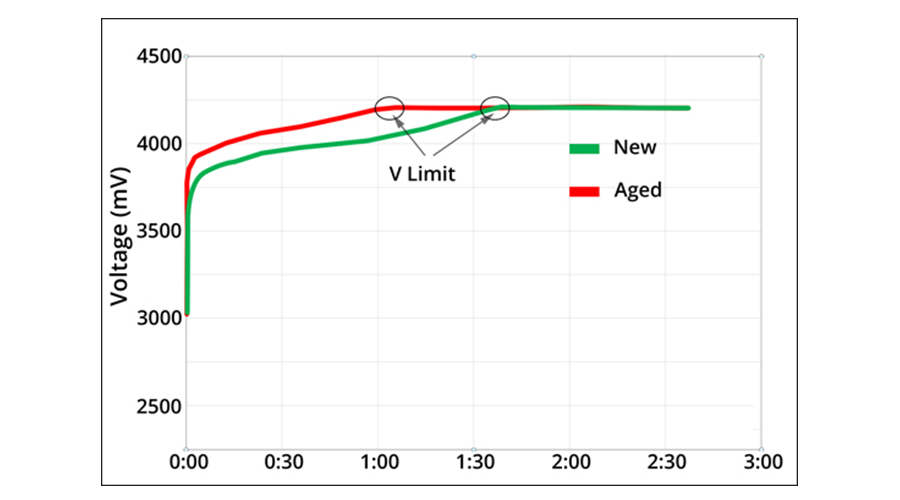
When charging a Li-ion battery, voltage rises quickly—similar to lifting a weight with a rubber band. A new battery (Figure 2) is “hungrier” and can absorb more energy before hitting the 4.20V/cell voltage limit. By contrast, an aged Li-ion battery reaches this voltage threshold much faster, often within 60 minutes.
Figure 2: Observing charge times of new and aged Li-ion in Stage 1 [1]
· New Li-ion battery: reaches full charge in ~90 minutes.
· Old Li-ion battery: reaches 4.20V/cell in ~60 minutes.
This means the newer battery has more “slack,” allowing it to accept charge longer before entering the saturation phase.
The Role of Saturation in Prolonged Charging
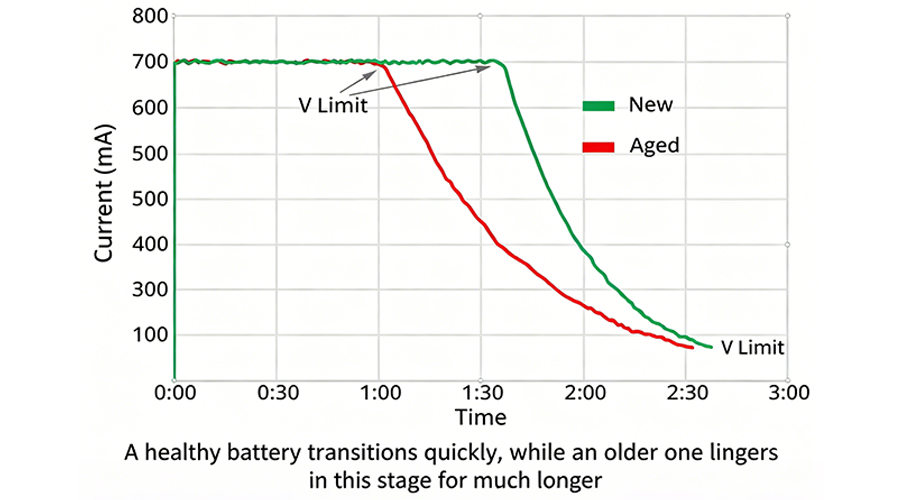
In Stage 2, the charging current tapers down gradually until it reaches about 0.05C to trigger ready mode. As shown in Figure 3, a healthy battery transitions quickly, while an older one lingers in this stage for much longer.
This explains why older Li-ion batteries take longer to charge despite having less total capacity. Think of it as a young athlete running a sprint versus an older person slowing down toward the finish line.
Figure 3: Observing saturation times of new and aged Li-ion in Stage 2 [1]
· New battery: shorter current trail, faster completion.
· Old battery: extended current trail, longer charge cycle.
Why Aging Slows Li-ion Charging: The Science Behind It
A common aging effect in Li-ion batteries is the loss of charge transfer capability. This happens due to the formation of passive materials on the electrodes, which:
· Reduce the porosity of electrodes
· Decrease surface area for reactions
· Lower ionic conductivity
· Increase migration resistance
These changes permanently affect performance and cannot be reversed.
Key Battery Health Indicators
The overall health of a Li-ion battery can be assessed based on three critical attributes:
- Capacity – the ability to store energy (primary indicator of battery health).
- Internal resistance – the ability to deliver current effectively.
- Self-discharge rate – reflects the mechanical integrity of the battery.
A good Li-ion battery absorbs most of the charge during Stage 1 and shows a short trailing time in Stage 2. By contrast, long trailing times are a sign of:
· Reduced capacity
· Higher internal resistance
· Elevated self-discharge
Can Battery Algorithms Help Diagnose Aging?
Advanced battery management algorithms can analyze differences between Stage 1 and Stage 2 charging behavior. By setting thresholds for capacity, internal resistance, and self-discharge, these systems can detect anomalies early.
Such smart diagnostic features are expected to become more common in future Li-ion battery chargers and management systems, helping users extend the lifespan of their devices and ensure charging safety.
Old Li-ion batteries take longer to charge because aging reduces their ability to transfer charge efficiently, leading to longer saturation phases despite reduced overall capacity. Understanding these charging behaviors not only helps explain performance decline but also guides better battery maintenance and replacement decisions.